|
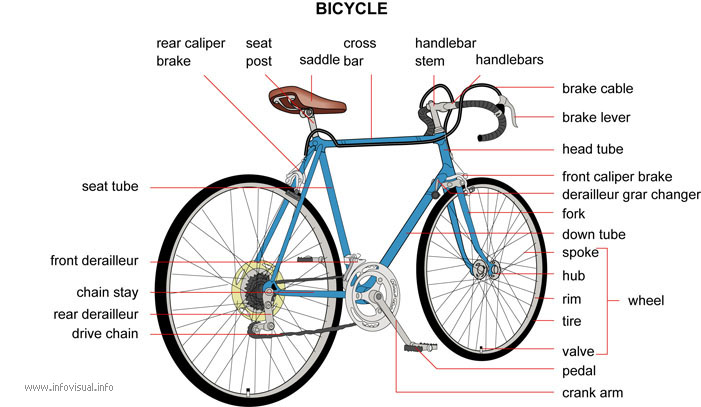
Bicycle: two-wheeled vehicle operated
by pedals.
Rear caliper brake: piece that joins the different parts of the
rear brake.
Seat post: metal tube that holds the seat.
Saddle: seat.
Cross bar: cylinder that connects the seat tube and the head
tube.
Handlebar stem: metal tube used to steer the front wheel.
handle bars: metal tube used for steering.
Brake cable: braided steel cable used to control the brakes.
Brake lever: device used to operate the brake.
Head tube: cylinder that holds the handlebars and which connects
the crossbar to the down tube.
Front caliper brake: piece that joins the different parts of
the front brake.
Derailleur gear changer: lever used to shift the chain on a multi-speed
bicycle.
Fork: piece formed of two parallel tubes, between which the wheel
is fixed.
Down tube: cylinder onto which the crank gear is attached and
which connects the down tube to the seat tube.
Spoke: long, thin piece of metal connecting the rim of a wheel
to its hub.
Hub: central part crossed by the axle.
Rim: circle of metal forming the edge of a wheel.
Tire: hollow, air-filled casing made of rubber-covered fabric
and steel.
Tire valve: system used to regulate the air in a tire.
Wheel: round object that turns around a central axle to allow
the bicycle to advance.
Pedal: footed operated system used to propel a bicycle.
Crank arm: arm perpendicular to an axle, used to give it circular
motion.
Drive chain: set of metal links that is used to transmit motion.
Rear derailleur: apparatus used to transfer the chain from one
gear to another, situated at the rear of a bicycle.
Chain stay: part on which the bicycle rests.
Front derailleur: apparatus used to transfer the chain from one
gear to another, situated at the front of a bicycle.
Seat tube: cylinder to which the seat is attached and which connects
the down tube to the crossbar.
|
![]()