|
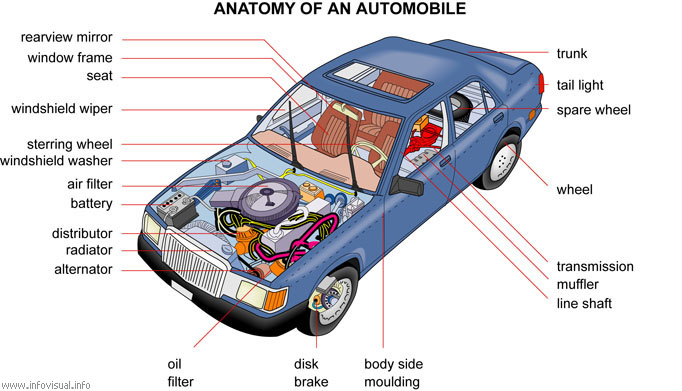
Anatomy of an automobile: road
vehicle that is motor-driven and is used for transporting people.
Trunk: place for stowing baggage.
Tail light: rear light.
Spare wheel: wheel of a car used to replace a damaged wheel.
Wheel: round object that turns around a central axel and allows
the car to advance.
Transmission: automobile apparatus that transmits mechanical
power to the wheels.
Muffler: device used to reduce engine noise.
Line shaft: axle on which mechanical power is transmitted to
the wheels.
Body side moulding: decorative moulding on the side of a car.
Disk brake: mechanism that slows and stops a car by friction,
by pressing a disk against the axel of a wheel.
Oil filter: device that removes impurities from oil passing through
it.
Alternator: generator that produces an alternating current.
Radiator: apparatus that cools the motor.
Distributor: case that is used to fire the cylinders.
Battery: device that generates electric current.
Air filter: device that remove impurities from air passing trough
it.
Windshield washer: liquid used to clean the windows.
Steering wheel: device used to handle a car in conjuction with
steering and gear systems.
Windshield wiper: movable device, made partly of rubber, that
wipes the windshield and rear window of a car.
Seat: type of armchair in the passenger compartment of a car.
Window frame: border around a window.
Rearview mirror: inside mirror used for looking backward.
|
![]()